++1913++18-08-2013+17-12-34+18-08-2013+17-12-34.jpg)
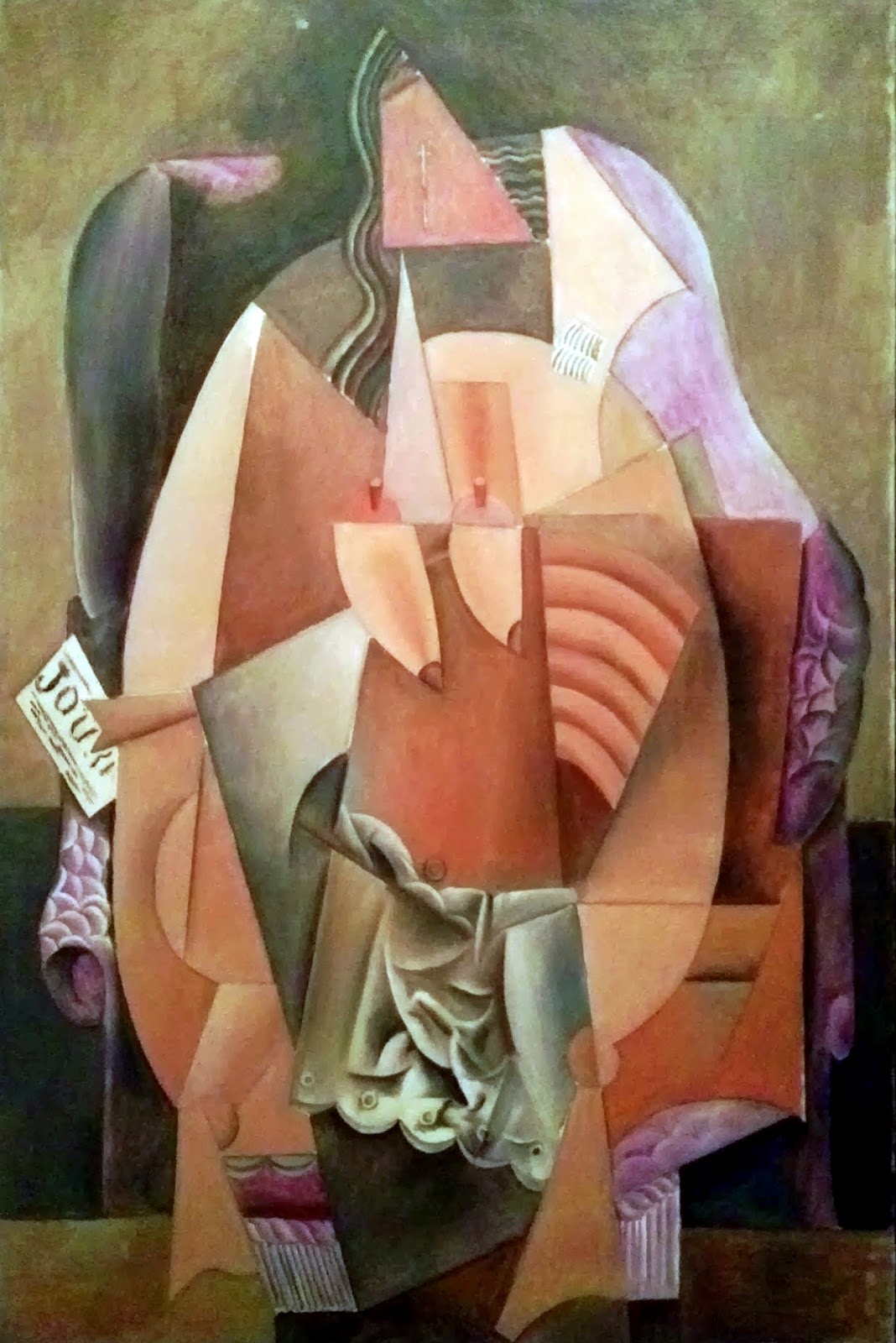
Braque tended to show objects exploding out or pulled apart into fragments, while Picasso rendered them magnetized, with attracting forces compelling elements of the pictorial space into the center of the composition. Analytical Cubists works were often very similar in appearance and style, but over time, their separate interests showed through. Their subject matter was restricted to the traditional genres of portraiture and still life ġ0. There was no realistic modelling of figures and objects were represented in space that employed small, tilted planes, set in a shallow space which flattens all surfaces into a single plane.ĩ. The suggestion of mood or object through colours could lead to ideas of theme or narrative or of symbolism-something Picasso and Braque avoided in order to concentrate to the formal experimentation of their paintings.Ĩ. Red and blue, for example, are colours with “moods,” yellow might be associated with an object, such as a lemon or the sun. Their limited use of colour avoided any reference to mood or emotion By reducing the palette, Picasso and Braque were able to paint in colours or tones, which were neutral in their associations.
From time to time, green will be used, but sparingly.ħ. These were basically Cézannian colours: ochre’s for the planes, black for the contours and white for the stippling on the surface. to better to maintain clarity between the forms’ fragmented planes.Ħ. They limited their palette to monochromatic earth tones and muted silvers, reducing the colour palette to several shades of one or two colours. Structure was paramount and colour was downplayed so that the viewer was not distracted.ĥ. Objects were displayed not in one place, in one time, in one space, within one light source, but from many vantage points.Ĥ. It was a conceptual image of the object, rather than an optical image – an intellectual experiment with structure. Analytical Cubism rejected Single point perspective and sought to show the object from multiple angles, and in differing lights. Objects were shown in a prismatic way so that the viewer can see all sides at once.ģ.

Objects and figures were broken down into geometric units, usually into two or three shapes by breaking the object down into fragments and then reassemble it.Ģ. Analytical Cubism was concerned with breaking down forms analytically into simplified geometric forms across the picture. GEORGES BRAQUE (1882-1963) ‘Violin and Jug’, 1910 (oil on canvas)Īnalytic Cubism 1910-1912 – Characteristicsġ. The History of Art reflects the social History of Mankind Great for Information on art movements, artists and theory of ArtĪ design blog publishing tips, tutorials and inspirations, as well as news and reviews for designers and developers. Synopsis: Artists, Movements and Styles in Modern Art c.1870 – 1975 Marvellous Art Musings interactively muses on twentieth century and contemporary South African art and showcases the vibrant South African art scene

Great for ideas on recycling art and green designs Guide to Modern Art – great research links, study notes. Understanding the use of Colour in Art and how we see colour Great Resource for South African Contemporary Artists Great Resource for Information on Art History


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
